
megaSoC
The Cortex-A53 is Arm's most widely deployed 64-bit Armv8-A processor.
Use the HAPS system.
Reference Design Comparison Table
This table will let you compare this reference design with others on SoC Labs| Title | megaSoC | milliSoC |
|---|---|---|
| Class | Complex | Mid-range |
| Reference Design | MegaSoC | TSRI/SoC Labs |
| Staffing | Academic team | Academic + dedicated post doc |
| Time Scales | 6 months to 1 year | 1+ years |
| Model Forms | Trial of processing element | |
| Tape Out / Package and Board Costs | >£50k | £25k-£50k |
| Processor(s) | A53 | M55/U55 |
| Processor(s) (speed) | > 800 Mhz | 250-800Mhz |
| Data Rates / On Chip Comms | <2.5 Gbps | 10-80 Gbps |
| Data Rates / Off Chip Comms | <50 Mbps | 0.1-0.8 Gbps |
| On Chip Memory Requirements | 32KB to multiple MB | 2MB+ |
| Virtual Prototype Environment | HAPS | MPS3 |
| Tape Out Node | 28nm | 28nm |
Related Projects and Workflows
This section details the following: the core reference design, the initial project that led to the definition of the reference design, and any additional projects that extend the reference design for new or additional applications. It also defines the related example workflows for the front end Architectural and Behavioural design stages, and the back end Logical and Physical design stages. Front end Behavioural design are usually accomplished with FPGA environments and tool chains, back end Physical design requires technology specific design rules and EDA tool suites.
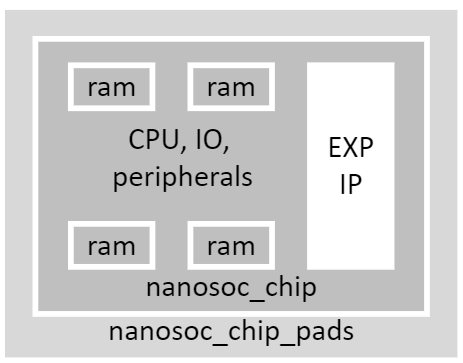
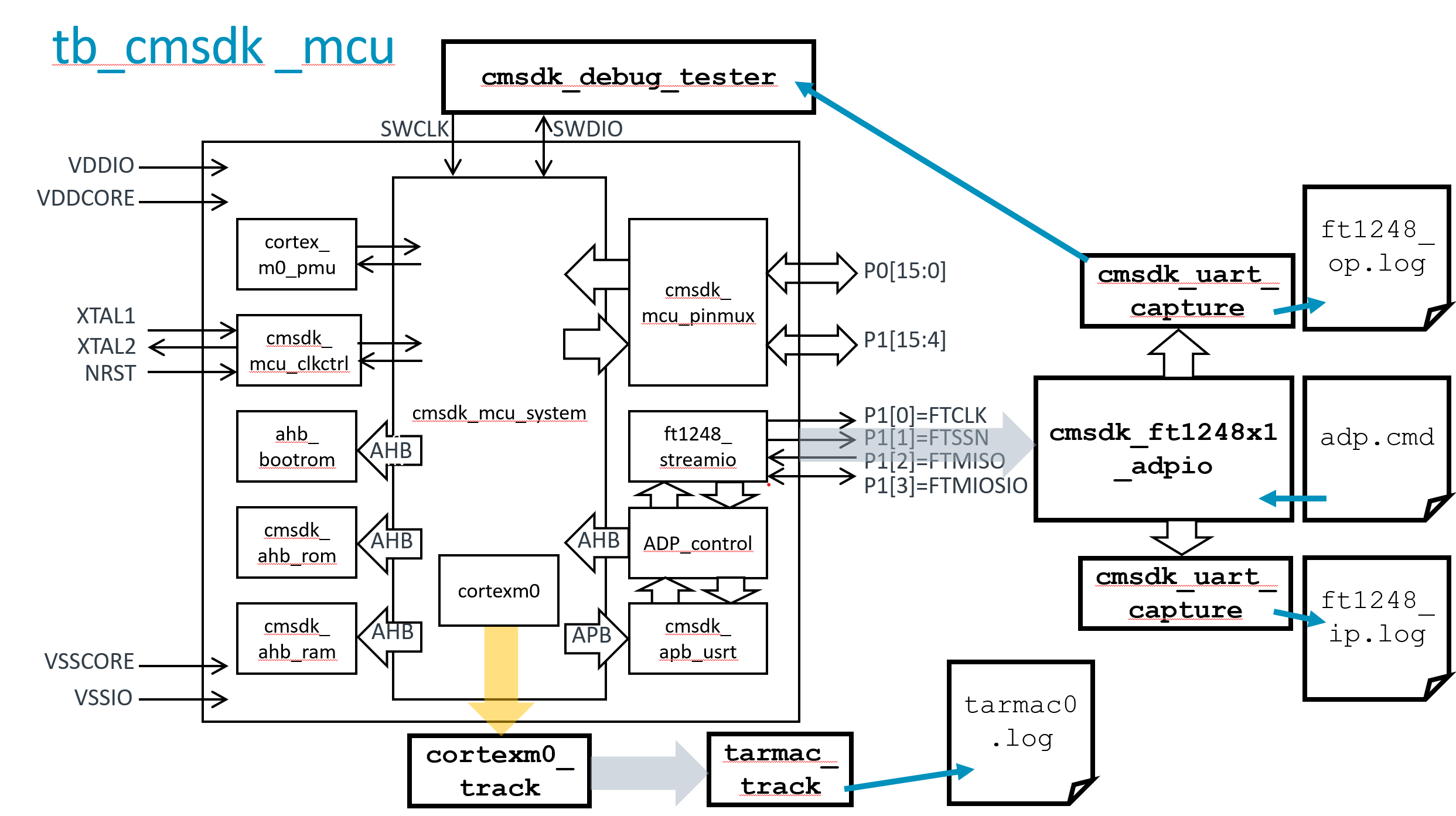
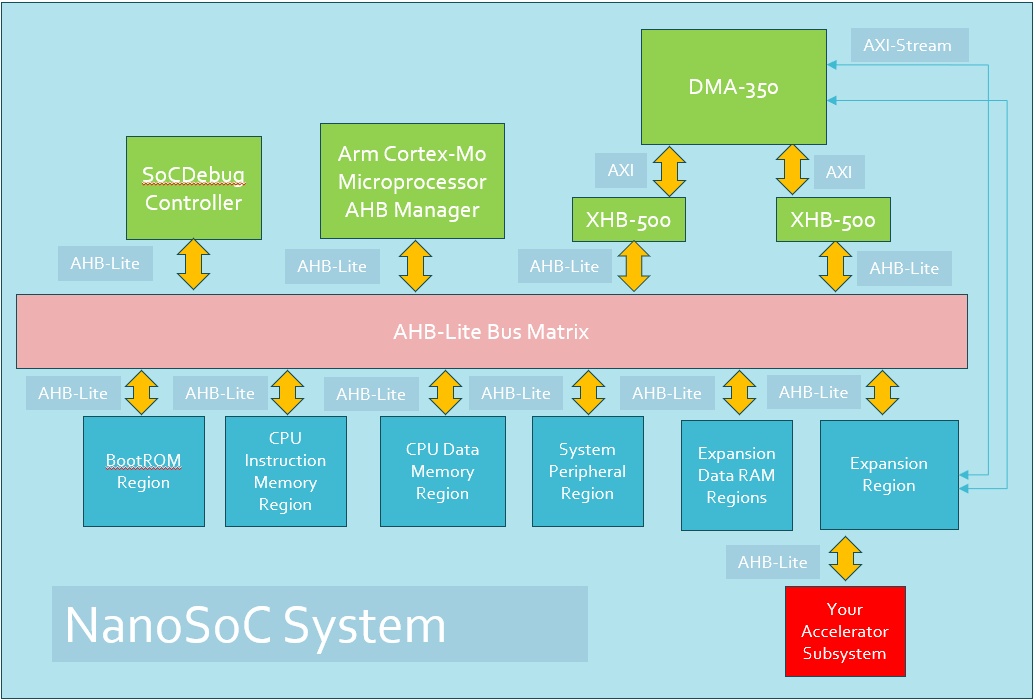
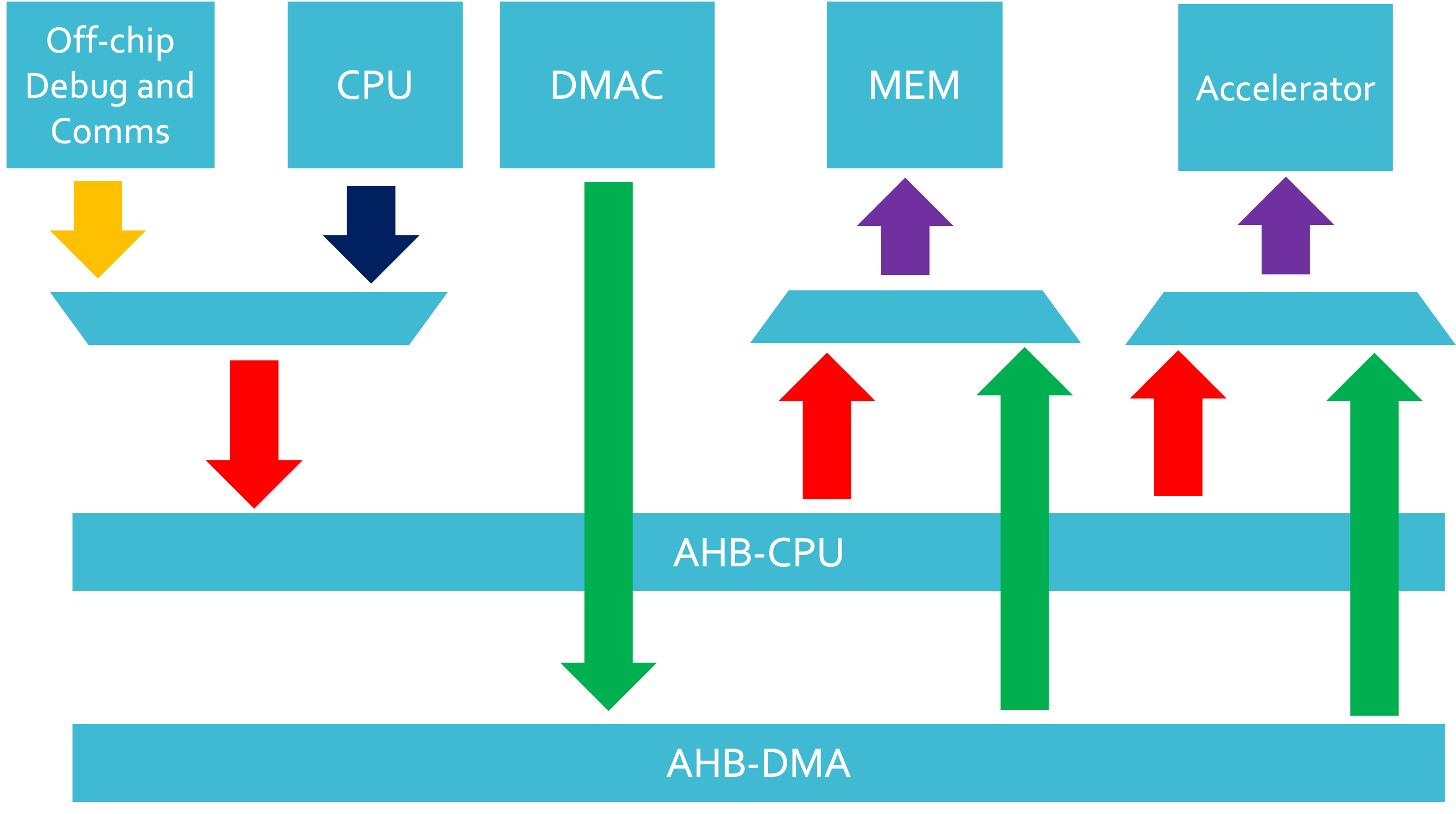
The integration of the DMA350 into the nanosoc re-usable SoC architecture will improve the transfer bandwidth on DMA channels within the SoC. This project integrates the DMA 350 into nanosoc, validates the integration and functionality of the DMA 350, and compares the performance of the DMA 350 to the PL230, that was the initial DMA controller integrated into nanosoc.

 David Flynn
David Flynn
 Daniel Newbrook
Daniel Newbrook
Comments
Testing comment
Does it send?
Add new comment
To post a comment on this article, please log in to your account. New users can create an account.